Project Task - Carousel Creator 7
1. Navigation Bar for Arrow Buttons
In the current carousel, there are arrow buttons that allow navigation to the previous and next pages. I will move these arrow buttons to the navigation bar. It seems better for the navigation bar below to be responsible for all carousel movements.
However, the existing carousel navigation component already handles navigation to the page corresponding to each navigation item when clicked. This means it already has the functionality to control the carousel pages, as confirmed by the props carouselIndex and setCarouselIndex.
Therefore, there is no need to change any props. All that needs to be done is to move the existing prevClick and nextClick functions, along with the buttons that triggered those functions on click events, to the carousel navigation component.
The modified CarouselNavigation component now appears as follows:
function CarouselNavigation({
items,
carouselIndex,
setCarouselIndex,
}: {
items: CarouselItemType[];
// Current index being displayed by the carousel
carouselIndex: CarouselIndexType;
setCarouselIndex: React.Dispatch<React.SetStateAction<CarouselIndexType>>;
}) {
// Function to determine the state of the button
const determineCarouselItemState = (itemIndex: number) => {
if (itemIndex === carouselIndex.currentIndex) {
return "active";
} else if (
/*
If the front or back page of the carousel is active
Even if it cannot place the active item in the center, fill 5 items
*/
carouselIndex.currentIndex === 0 ||
carouselIndex.currentIndex === 1
) {
return itemIndex < 5 ? "pending" : "inactive";
} else if (
carouselIndex.currentIndex === items.length - 1 ||
carouselIndex.currentIndex === items.length - 2
) {
return itemIndex >= items.length - 5 ? "pending" : "inactive";
} else {
return carouselIndex.currentIndex - 2 <= itemIndex &&
itemIndex <= carouselIndex.currentIndex + 2
? "pending"
: "inactive";
}
};
// Function to navigate to a specific index page
const onCarouselNavigationItemClick = (itemIndex: number) => {
setCarouselIndex((prev) => {
if (prev.currentIndex === itemIndex) {
return prev;
} else {
return {
previousIndex: prev.currentIndex,
currentIndex: itemIndex,
};
}
});
};
const handlePrevClick = () => {
setCarouselIndex((prev) => ({
previousIndex: prev.currentIndex,
currentIndex: (prev.currentIndex - 1 + items.length) % items.length,
}));
};
const handleNextClick = () => {
setCarouselIndex((prev) => ({
previousIndex: prev.currentIndex,
currentIndex: (prev.currentIndex + 1) % items.length,
}));
};
return (
<dl className="flex flex-row w-full h-10">
<button onClick={handlePrevClick} className="z-10 h-full">
<IoIosArrowBack className="text-gray-500" size={30} />
</button>
{items.map((item, index) => (
<CarouselNavigationItem
key={index}
item={item}
itemState={determineCarouselItemState(index)}
onItemClick={() => {
onCarouselNavigationItemClick(index);
}}
/>
))}
<button onClick={handleNextClick} className="z-10 h-full">
<IoIosArrowForward className="text-gray-500" size={30} />
</button>
</dl>
);
}
Let’s move the determineCarouselItemState function outside the component as well. The function will be modified and moved outside the component, adjusting its arguments appropriately when used in the CarouselNavigationItem component.
// Function to determine the state of the button
function determineCarouselItemState(
itemIndex: number,
carouselCurrentIndex: number,
carouselTotalLength: number
) {
if (itemIndex === carouselCurrentIndex) {
return "active";
} else if (carouselCurrentIndex === 0 || carouselCurrentIndex === 1) {
return itemIndex < 5 ? "pending" : "inactive";
} else if (
carouselCurrentIndex === carouselTotalLength - 1 ||
carouselCurrentIndex === carouselTotalLength - 2
) {
return itemIndex >= carouselTotalLength - 5 ? "pending" : "inactive";
} else {
return carouselCurrentIndex - 2 <= itemIndex &&
itemIndex <= carouselCurrentIndex + 2
? "pending"
: "inactive";
}
}
Next, we will remove the prevClick and nextClick functions as well as the arrow buttons that triggered these functions from the carousel component. When rendering the carousel now, the arrow buttons will be integrated into the navigation bar and the page transition functionality will also work seamlessly.
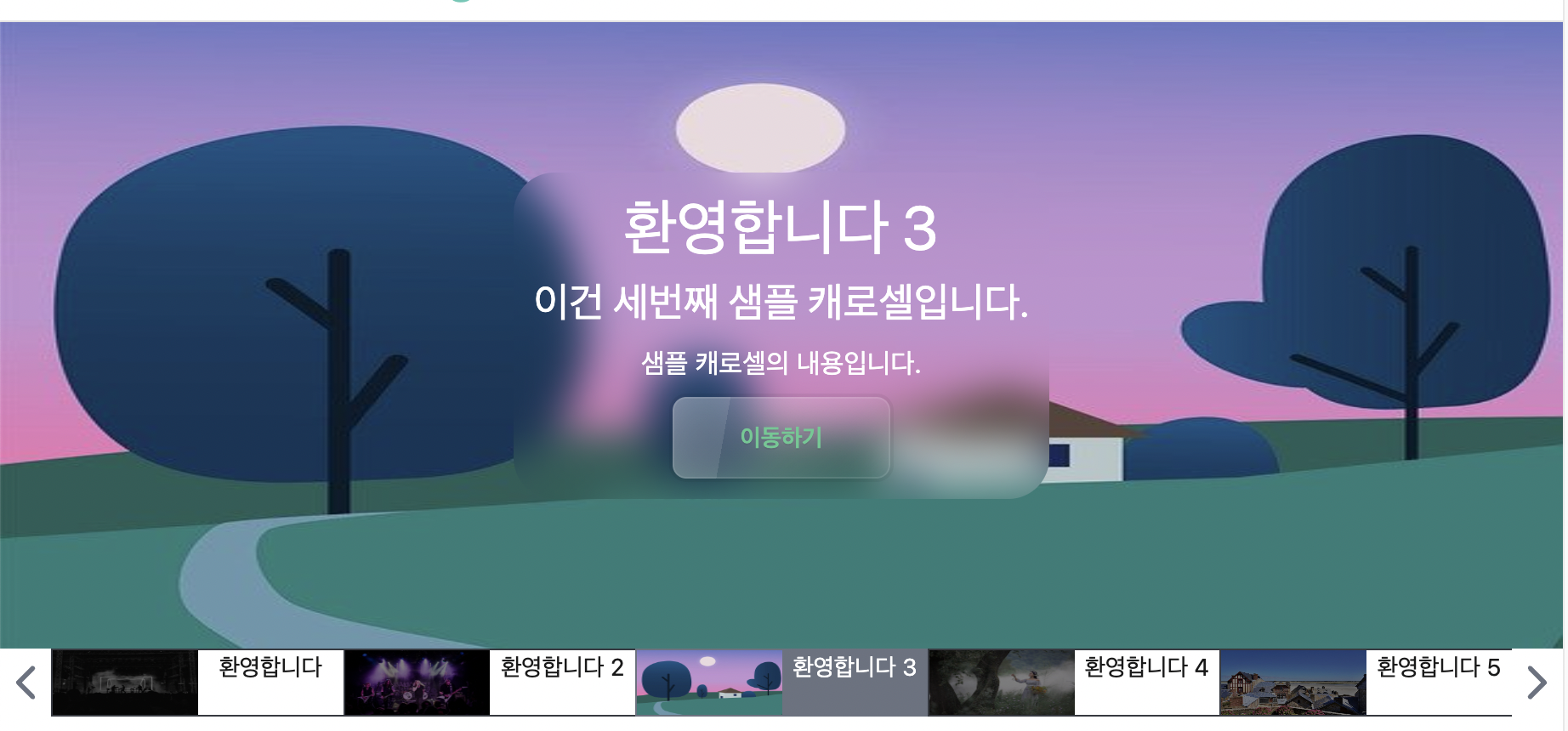
2. Carousel Navigation Design Renewal
2.1 Navigation Bar Design
The current navigation bar looks quite unattractive. Therefore, I plan to renew it as much as possible, referring to the carousel design on the MapleStory main page.
First, I will include the navigation bar inside the carousel. Since the current carousel page components are managed with absolute positioning, they do not take up space within the layout, so we can think of just placing the navigation bar.
Thus, we will introduce the CarouselNavigation component inside the div element wrapping the carousel and add the items-center class to position it at the bottom. The structure of the carousel component will look as follows:
<section>
<div
className="relative flex flex-row items-end justify-between w-full h-[60vh]"
onTouchStart={handleTouchStart}
onTouchMove={handleTouchMove}
>
{/* These CarouselItems do not occupy layout space because they have absolute positioning */}
{items.map((item, index) => (
<CarouselItem
key={item.id}
item={item}
itemState={determineCarouselItemState(index)}
/>
))}
<CarouselNavigation
items={items}
carouselIndex={carouselIndex}
setCarouselIndex={setCarouselIndex}
/>
</div>
</section>
Next, we will change the color of the carousel navigation bar and add opacity so that the images displayed in the carousel slightly show beyond the navigation bar. This will help indicate that the navigation bar is part of the carousel. Consequently, the color of the arrows will also be modified, and the height of the navigation bar will be set to be relative to the height of the carousel. Additionally, we will set the z-index to prevent the carousel images from obscuring the navigation bar.
The dl tag will have the classes h-[10%] bg-gray-400/70 z-20, and the color of the arrow buttons will be set to the text-gray-300 class. The completed navigation bar component is as follows:
function CarouselNavigation({
items,
carouselIndex,
setCarouselIndex,
}: {
items: CarouselItemType[];
// Current index being displayed by the carousel
carouselIndex: CarouselIndexType;
setCarouselIndex: React.Dispatch<React.SetStateAction<CarouselIndexType>>;
}) {
// Function to navigate to a specific index page
const onCarouselNavigationItemClick = (itemIndex: number) => {
setCarouselIndex((prev) => {
if (prev.currentIndex === itemIndex) {
return prev;
} else {
return {
previousIndex: prev.currentIndex,
currentIndex: itemIndex,
};
}
});
};
const handlePrevClick = () => {
setCarouselIndex((prev) => ({
previousIndex: prev.currentIndex,
currentIndex: (prev.currentIndex - 1 + items.length) % items.length,
}));
};
const handleNextClick = () => {
setCarouselIndex((prev) => ({
previousIndex: prev.currentIndex,
currentIndex: (prev.currentIndex + 1) % items.length,
}));
};
return (
<dl className="flex flex-row w-full h-[10%] bg-gray-400/70 z-20">
<button onClick={handlePrevClick} className="z-10 h-full">
<IoIosArrowBack className="text-gray-300" size={30} />
</button>
{items.map((item, index) => (
<CarouselNavigationItem
key={index}
item={item}
itemState={determineCarouselItemState(
index,
carouselIndex.currentIndex,
items.length
)}
onItemClick={() => {
onCarouselNavigationItemClick(index);
}}
/>
))}
<button onClick={handleNextClick} className="z-10 h-full">
<IoIosArrowForward className="text-gray-300" size={30} />
</button>
</dl>
);
}
2.2 CarouselNavigationItem Design
Next, I will design each item in the navigation. First, I will remove the unattractive borders from all navigation items and position them appropriately with proper spacing within the navigation bar. Additionally, for the active item, I will make the image brighter and add a green border to emphasize it. The text color will also be modified.
The updated CarouselNavigationItem component will look like this:
function CarouselNavigationItem({
item,
itemState,
onItemClick,
}: {
item: CarouselItemType;
itemState: string;
onItemClick: () => void;
}) {
// active refers to the button state corresponding to the item currently displayed in the carousel
// pending refers to the button state that is visible but not active
const carouselItemConfig: { [key: string]: string } = {
active: "text-base-100 hover:bg-gray-600",
pending:
"brightness-50 text-gray-500 hover:brightness-100 hover:bg-gray-400",
inactive: "hidden",
};
return (
<button
onClick={onItemClick}
className={`flex-1 flex flex-row mx-1 items-center transition-all duration-700 ${carouselItemConfig[itemState]}`}
>
<dt
className={`flex-1 w-full h-full ${
itemState === "active" ? "py-1.5 px-1" : "p-2"
}`}
>
<img
className={`object-fill w-full h-full ${
itemState === "active" ? "border-2 border-primary" : ""
}`}
src={item.image}
alt={`carousel-item-${item.id}`}
/>
</dt>
<dd className="flex-1 text-sm">{item.title}</dd>
</button>
);
}
Now, we can observe a better appearance of the carousel navigation.
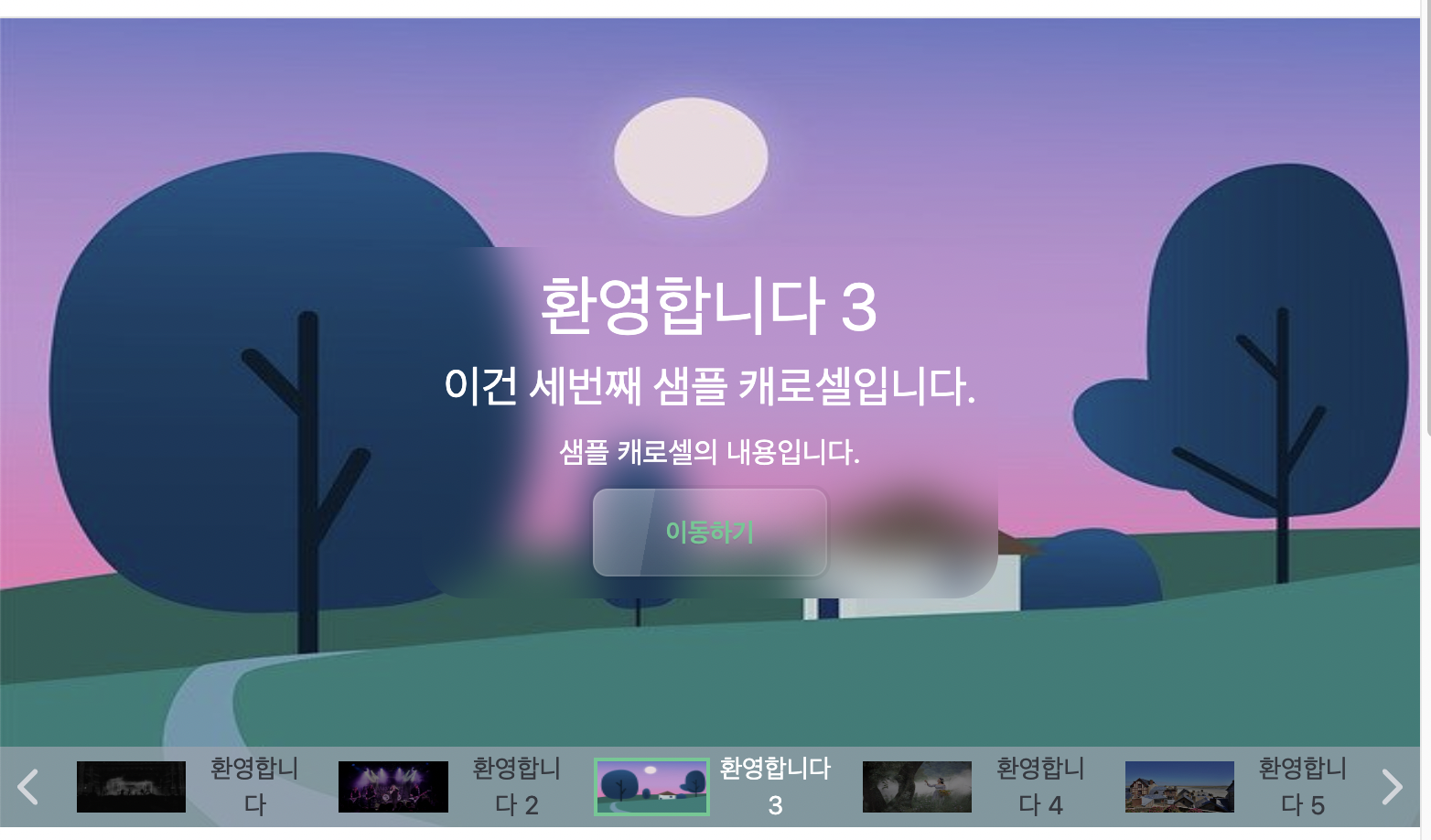
2.3 Mobile View Adjustment
However, there is still an issue with the navigation bar. The view varies too much depending on the screen size. For example, on larger screens, the navigation appears less attractive.
While I can overlook the issues that arise on large screens, the most significant problem is with mobile screens. The navigation bar is too small to properly view the items.
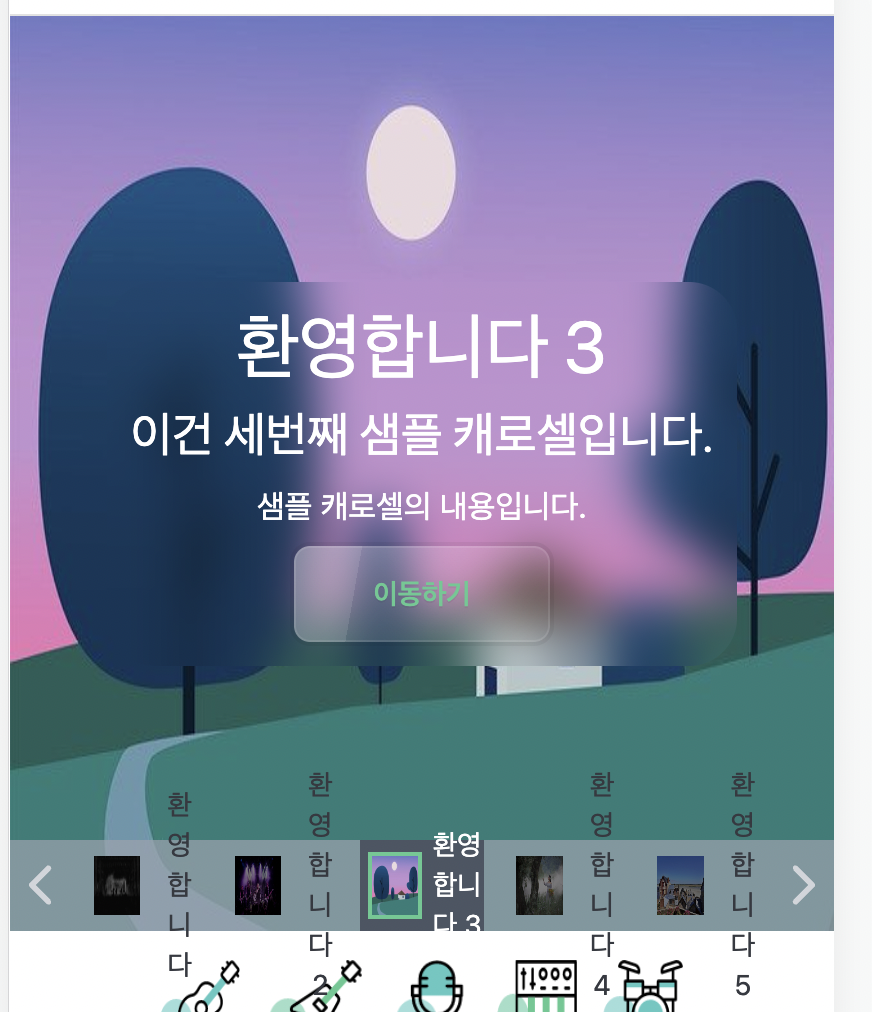
This was resolved in a simple but less sophisticated way by preventing the images from being displayed in the navigation bar on mobile screens. Tailwind provides an easy way to implement responsive design, which allowed for a straightforward solution.
In the CarouselNavigationItem, I set the dt tag containing the images to be hidden by default (equivalent to display: none) and configured it to be visible only when the screen width is 768px or more. Here is the relevant code, with changes only appearing in the dt tag.
function CarouselNavigationItem({
item,
itemState,
onItemClick,
}: {
item: CarouselItemType;
itemState: string;
onItemClick: () => void;
}) {
// active refers to the button state corresponding to the item currently displayed in the carousel
// pending refers to the button state that is visible but not active
const carouselItemConfig: { [key: string]: string } = {
active: "text-base-100 hover:bg-gray-600",
pending:
"brightness-50 text-gray-500 hover:brightness-100 hover:bg-gray-400",
inactive: "hidden",
};
return (
<button
onClick={onItemClick}
className={`flex-1 flex flex-row mx-1 items-center transition-all duration-700 ${carouselItemConfig[itemState]}`}
>
<dt
className={`hidden md:block flex-1 w-full h-full ${
itemState === "active" ? "py-1.5 px-1" : "p-2"
}`}
>
<img
className={`object-fill w-full h-full ${
itemState === "active" ? "border-2 border-primary" : ""
}`}
src={item.image}
alt={`carousel-item-${item.id}`}
/>
</dt>
<dd className="flex-1 text-sm">{item.title}</dd>
</button>
);
}
With this change, images will no longer be visible in the navigation bar on mobile screens. Although it may appear less attractive, it is better than having text overflow beyond the navigation bar.
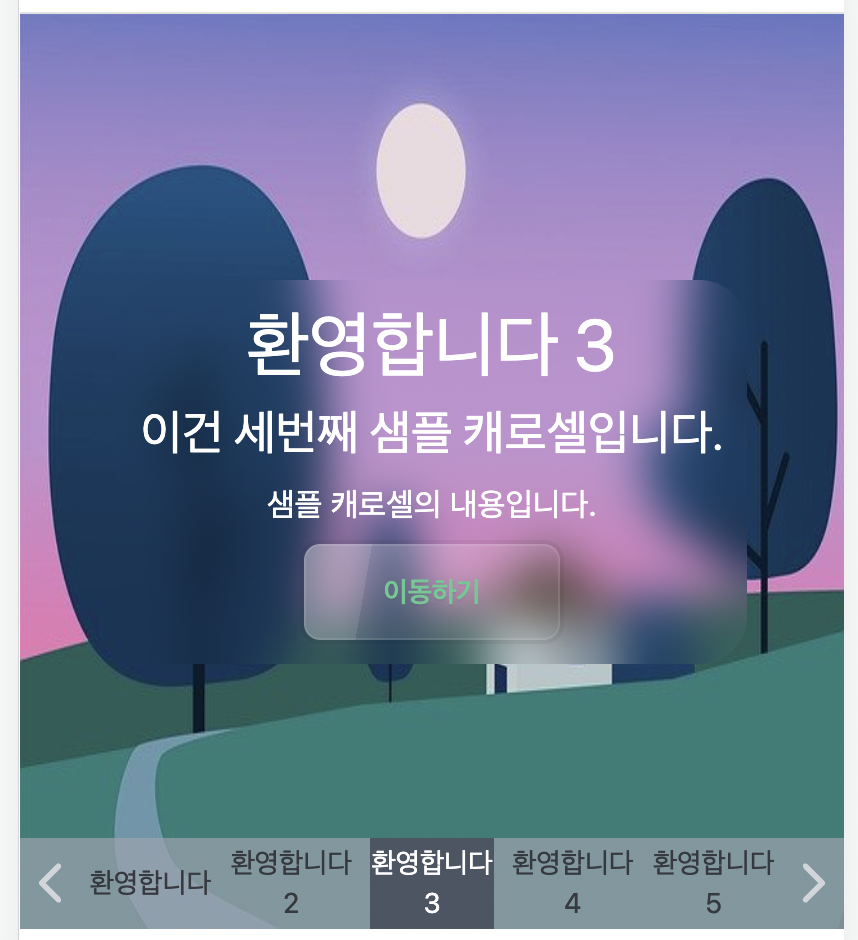
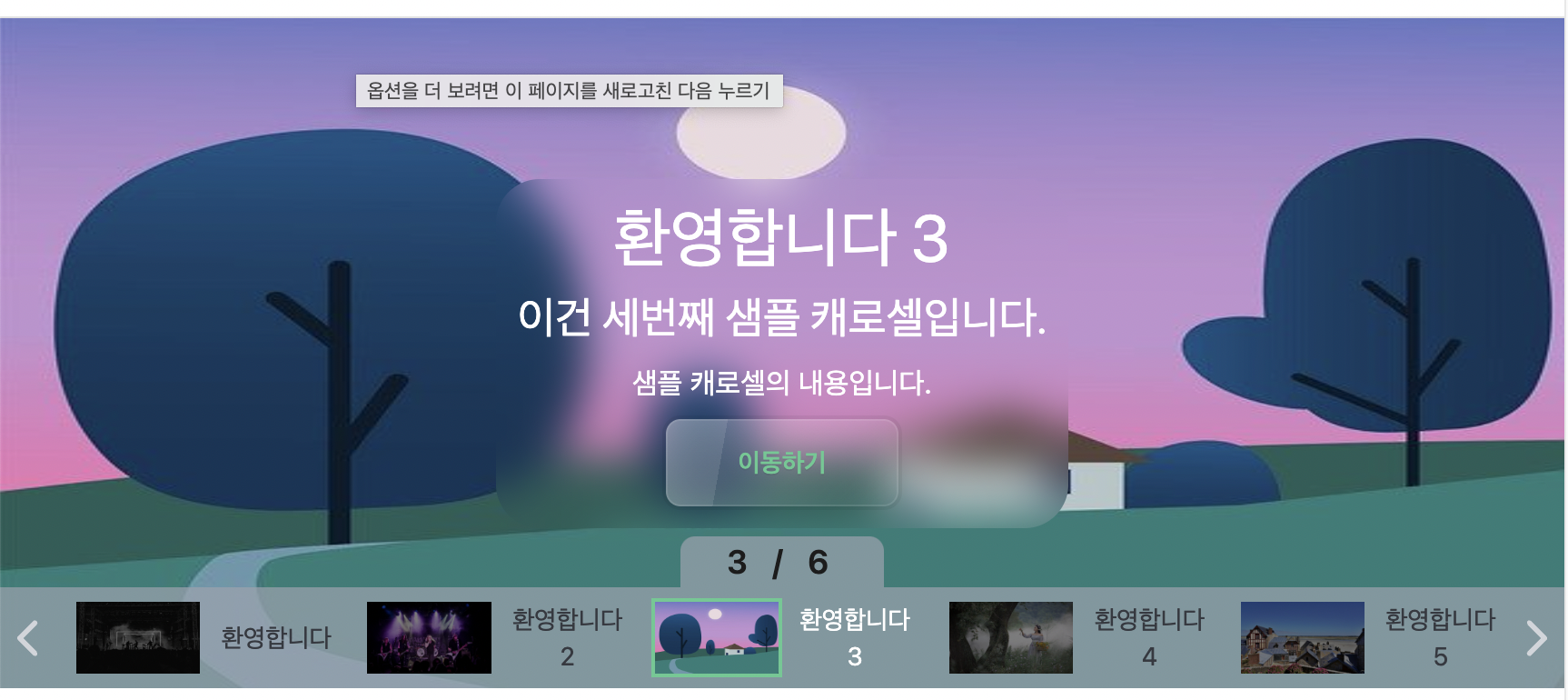
3. Display Page Numbers on the Navigation Bar
This can be easily implemented since the carousel navigation receives the current index and total items as props. Positioning can be handled using absolute positioning, and the rest of the design can match the style and size of the navigation bar items.
The following button can be added inside the dl tag of the CarouselNavigation component.
<button className="absolute bottom-[15%] btn btn-xs bg-gray-400/70 hover:bg-gray-400 w-28 h-7 z-30 border-none rounded-none rounded-t-lg text-lg tracking-[0.3rem]">
{carouselIndex.currentIndex + 1} / {items.length}
</button>
This will display the page number as follows.
4. Automatic Transition Every Few Seconds
This can be easily achieved using the setInterval function. By setting an interval in the useEffect of the carousel component, the carousel can automatically transition to the next index at set intervals.
The following code should be added to the Carousel component. This will transition the carousel screen every 3 seconds.
useEffect(() => {
const carouselTimer = setInterval(() => {
setCarouselIndex((prev) => ({
previousIndex: prev.currentIndex,
currentIndex: (prev.currentIndex + 1) % items.length,
}));
}, 3000);
return () => {
clearInterval(carouselTimer);
};
}, []);
References
Using setInterval https://ko.javascript.info/settimeout-setinterval
Creating the Perfect Carousel Part 1 https://code.tutsplus.com/ko/tutorials/create-the-perfect-carousel-part-1--cms-29481