Setting Up NodeJS and Prisma Backend Testing Environment
This document is in progress.
Introduction
This article follows up on Deploying MySQL, Prisma, and NodeJS Server to Google Cloud Platform. This time, let's add tests to the project.
I was primarily developing the front-end and a bit of the back-end, and it became cumbersome to manually check each modification through Postman every time. Therefore, I decided to implement tests that I had only heard about.
For the technology stack, the back-end utilizes MySQL, Prisma ORM, NodeJS, and Express, while the front-end is built with Next.js version 12.
Basic Setup
Installation and Configuration
I intended to use Jest, but encountered issues with module support. Therefore, I decided to use Vitest instead, which is compatible.
npm install --save-dev vitest
Next, add the following test script to your package.json.
{
"scripts": {
"test": "vitest"
}
}
Then, create a Vitest configuration file and configure it to test files with .test.js or .test.ts extensions located in the __tests__ folder.
// vitest.config.js
import { defineConfig } from "vitest/config";
export default defineConfig({
test: {
include: ["__tests__/*.test.(js|ts)"],
},
});
Basic Testing
Let's start by creating a simple function and testing it. Create a file named utils/sample.js and write the following code. This function receives n and returns an array of powers of 2 up to 2^n.
// utils/sample.js
function powersOfTwo(n) {
return [...Array(n + 1)].map((_, i) => 2 ** i);
}
export { powersOfTwo };
Next, create a file named __tests__/sample.test.js and write the following code to test simple addition and the powersOfTwo function.
import { expect, it, describe } from "vitest";
import { powersOfTwo } from "utils/sample";
describe("Sample Test", () => {
it("1 + 1 = 2", () => {
expect(1 + 1).toBe(2);
});
it("2 + 1 = 3", () => {
expect(2 + 1).toBe(3);
});
});
describe("Basic Tests", () => {
it("Testing for fixed tests", () => {
expect(powersOfTwo(0)).toEqual([1]);
expect(powersOfTwo(1)).toEqual([1, 2]);
expect(powersOfTwo(4)).toEqual([1, 2, 4, 8, 16]);
});
});
Run npm test, and you will see that the tests execute successfully as expected.
$ npm test
> [email protected] test
> vitest
DEV v1.6.0 /Users/kimsunghyun/Desktop/sinchon-admin-service/admin-service-new-backend
✓ __tests__/sample.test.js (3)
✓ Sample Test (2)
✓ 1 + 1 = 2
✓ 2 + 1 = 3
✓ Basic Tests (1)
✓ Testing for fixed tests
Test Files 1 passed (1)
Tests 3 passed (3)
Start at 18:20:57
Duration 144ms (transform 19ms, setup 0ms, collect 10ms, tests 3ms, environment 0ms, prepare 48ms)
PASS Waiting for file changes...
press h to show help, press q to quit
Setting up a Testing Database
However, we are not testing just JS functions. First, we need to test if the DB is correctly handled in the backend, and ultimately, verify the connection between the front-end and backend. Therefore, let’s set up a testing database.
Create Container
We decided to use MySQL as the testing database. Let's create a MySQL container using Docker. Since this will run locally, I set the DB name to testdb and the password to testpassword for simplicity. Additionally, I configured it to be accessible on port 3307.
docker run --name mysql-test -e MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=testpassword -e MYSQL_DATABASE=testdb -p 3307:3306 -d mysql:latest
Configure Testing Database
In the prisma/schema.prisma file, set the database URL to utilize environment variables.
// prisma/schema.prisma
datasource db {
provider = "mysql"
url = env("DATABASE_URL")
}
Create a .env.test file and set the DB URL as follows. The production URL is, of course, in the .env file. Set the testing database URL in .env.test.
DATABASE_URL="mysql://root:testpassword@localhost:3307/testdb"
Now let's create the necessary tables in the testing DB. Using the prisma migrate command will generate a migration file in the prisma/migrations folder, allowing us to create tables in the DB.
npx prisma migrate dev --name init
You may encounter an error here because prisma migrate will use the DATABASE_URL from the project’s .env file.
Therefore, temporarily change the DATABASE_URL in the .env file to that of the .env.test file or directly include the DATABASE_URL in the package.json scripts or schema.prisma. Ultimately, ensure that the URL to testdb is correctly set. You might also consider using dotenv-cli for this purpose.
Next, configure it to use .env.test when testing. Install dotenv-cli to set the environment variable file in the script.
npm install --save-dev dotenv-cli
Modify the package.json as follows to use the .env.test file as the environment variable during testing.
{
"scripts": {
"test": "dotenv -e .env.test -- vitest"
}
}
Setting Up Seed Data
With the Docker container for the testing DB up and running and the tables created via prisma migrate, let's insert some seed data. Create a file named prisma/seed-test.js and write the following code to delete all existing data in the tables.
import { PrismaClient } from "@prisma/client";
const prisma = new PrismaClient();
async function main() {
// Deleting existing data
await prisma.admin.deleteMany();
await prisma.student.deleteMany();
await prisma.semester.deleteMany();
await prisma.lecture.deleteMany();
await prisma.studentLectureLog.deleteMany();
await prisma.weeklyAttendLog.deleteMany();
}
export default function setup() {
main()
.then(async () => {
await prisma.$disconnect();
})
.catch(async (e) => {
console.error(e);
await prisma.$disconnect();
process.exit(1);
});
}
Edit the vitest.config.js file to execute the seed-test.js file prior to testing. In globalSetup, it executes the function exported as default from the provided files.
import { defineConfig } from "vitest/config";
export default defineConfig({
test: {
include: ["__tests__/*.test.(js|ts)"],
globalSetup: ["prisma/seed-test.js"],
},
});
Writing Test Code
Now let's write the test code. Create a file named __tests__/student.test.js and write the following code. It sets up the connection to the testing database within the test file and includes a simple test case. The function for creating a student utilizes the pre-defined StudentRepository.
import { PrismaClient } from "@prisma/client";
import { afterAll, beforeAll, describe, it, expect } from "vitest";
import StudentRepository from "../repositories/student_repository";
const prisma = new PrismaClient();
beforeAll(async () => {
await prisma.$connect();
});
afterAll(async () => {
await prisma.$disconnect();
});
describe("StudentRepository", () => {
it("creates student", async () => {
expect(
await StudentRepository.createStudent({
name: "John Doe",
bojHandle: "JohnDoe",
school: "SOGANG",
email: "[email protected]",
phone: "01000001111",
studentNumber: "2021-12345",
paymentStatus: "PAID_30000",
}),
).toMatchObject({ bojHandle: "JohnDoe", email: "[email protected]" });
});
});
Run npm run test, and the tests will execute as shown below. Ensure that the MySQL container is running properly.
$ npm test
> [email protected] test
> dotenv -e .env.test -- vitest
DEV v1.6.0 /Users/kimsunghyun/Desktop/sinchon-admin-service/admin-service-new-backend
stdout | __tests__/student.test.js > StudentRepository > creates student
{ url: 'mysql://root:testpassword@localhost:3307/testdb' }
✓ __tests__/sample.test.js (3)
✓ __tests__/student.test.js (1)
Test Files 2 passed (2)
Tests 4 passed (4)
Start at 00:47:12
Duration 339ms (transform 42ms, setup 0ms, collect 70ms, tests 43ms, environment 0ms, prepare 131ms)
PASS Waiting for file changes...
press h to show help, press q to quit
Automating with Docker Compose
Now, let's create a docker-compose.test.yml file to automate the creation of the testing DB. Write the Docker Compose file as follows.
version: "3.8"
services:
db:
image: mysql:8.0
ports:
- 3307:3306
env_file:
- .env.test
environment:
TZ: Asia/Seoul
MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD: testpassword
MYSQL_DATABASE: testdb
volumes:
- mysql_test_data:/var/lib/mysql
volumes:
mysql_test_data:
Now you can execute the following scripts to run your tests. Using docker compose down makes it easy to clean up the containers.
docker compose -f docker-compose.test.yml up -d
npm run migrate:test
npm run test
docker compose -f docker-compose.test.yml down
Add these commands as scripts in your package.json.
{
"scripts": {
"test": "dotenv -e .env.test -- vitest",
"migrate:test": "dotenv -e .env.test -- npx prisma migrate deploy",
"test:docker": "docker-compose -f docker-compose.test.yml up -d && npm run migrate:test && npm run test && docker-compose -f docker-compose.test.yml down",
// ...
}
}
Now, when you run npm run test:docker, it will automatically create the testing DB, perform migrations, execute tests, and clean up the DB.
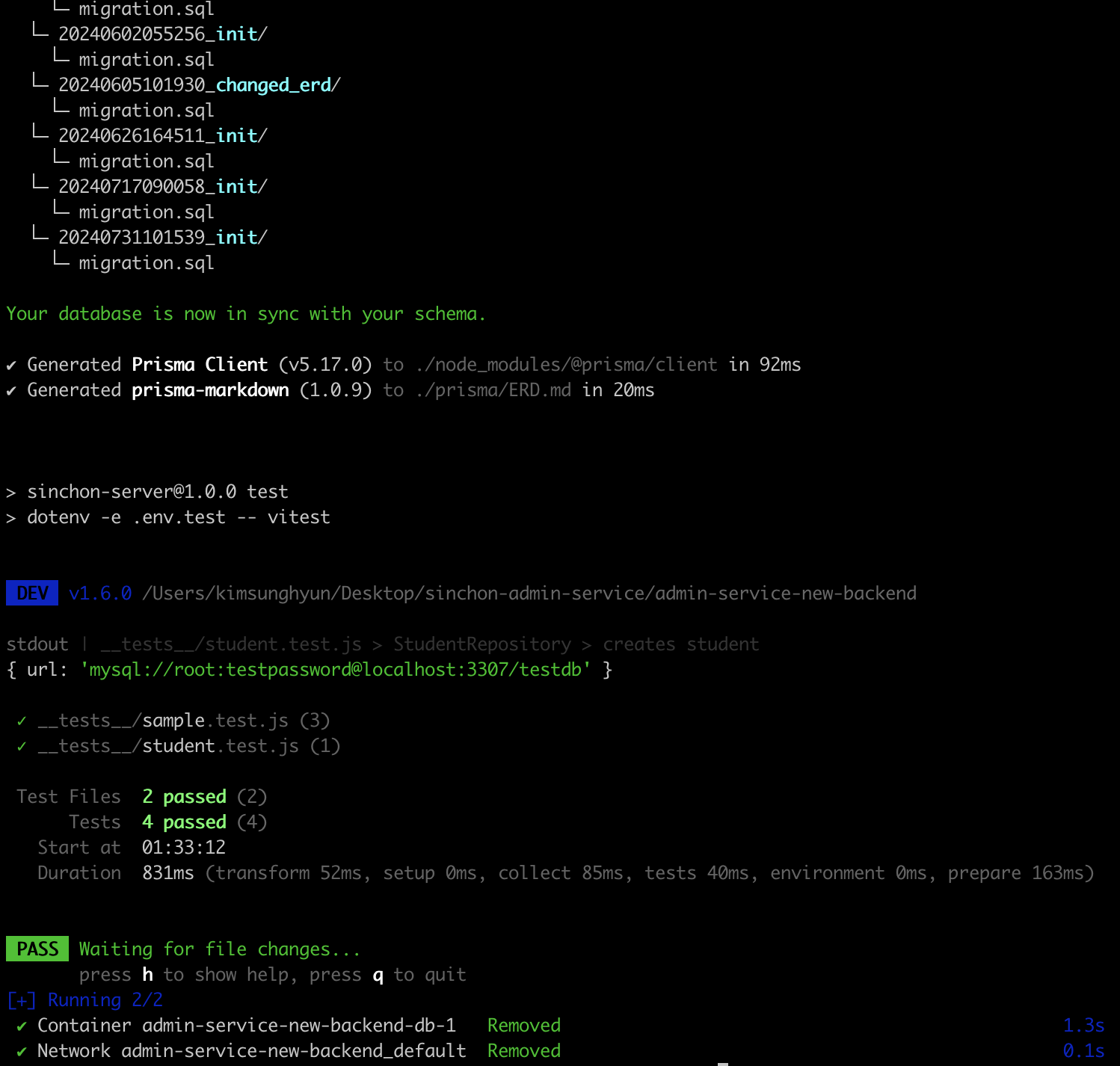
Troubleshooting
However, an issue arises. An error repeatedly occurs as follows. This error does not happen when executing commands directly, but it happens when running npm run test:docker.
Error: P1017: Server has closed the connection.
Interestingly, when this error occurs and the command exits, running npm run test:docker again does not produce the error this time. The commands complete successfully, and after executing docker-compose down, running npm run test:docker again results in the error repeating.
The issue can be summarized as follows:
npm run test:dockeris executed.- The first command in the script,
docker-compose -f docker-compose.test.yml up -d, is executed. - The MySQL container for testing is launched.
npm run migrate:testexecutes.- Prisma migrate runs but fails because the MySQL container expected to run in Docker Compose may not be fully ready.
- Therefore, an error occurs indicating that the server cannot be accessed, and the script terminates without executing
docker-compose down, leaving the MySQL container running. - The next run of
npm run test:dockersucceeds since the MySQL container is already running.
To resolve this, we need to ensure that Prisma migrate executes only after the MySQL container is fully prepared. We will use the wait-for-it script for this purpose.
First, download the wait-for-it.sh file from the wait-for-it GitHub repository. Create a bin/ folder at the project root and place the wait-for-it.sh file inside.
Now, create a file named bin/run-test.sh and write the following code. This script checks if the MySQL container is prepared before executing the commands.
#!/bin/bash
# Run Docker Compose to launch the container
docker-compose -f docker-compose.test.yml up -d
# Wait for the database to be ready for 60 seconds
./wait-for-it.sh localhost:3307 -t 60
# Execute migration after the database is ready
npm run migrate:test
# Run tests
npm run test
# Shutdown the container after the tests are complete
docker-compose -f docker-compose.test.yml down
Modify the test:docker script in the package.json as follows.
{
"scripts": {
// existing scripts...
"test:docker": "./bin/run-test.sh",
// ...
}
}
Now, executing this script will ensure that Prisma migrate runs only after the MySQL container is prepared, avoiding the errors. If it does not execute, make sure to give it execute permission.
chmod +x bin/run-test.sh
Running npm run test:docker will create the testing DB, perform migrations, execute tests, and then clean up the DB automatically. The wait-for-it.sh script helps maintain the order of operations: starting the DB, running migrations, and executing tests.
Configure Sequential Test Execution
After setting up and running the tests, I encountered many errors. Vitest runs tests in parallel by default, which caused conflicts during data generation and deletion for each test when using an actual Docker DB. Therefore, let's configure the tests to run sequentially.
This can be done simply by setting fileParallelism to false in the Vitest configuration file. Modify the vitest.config.js as follows.
// vitest.config.js
import { defineConfig } from "vitest/config";
export default defineConfig({
test: {
include: ["__tests__/**/*.test.(ts)"],
fileParallelism: false,
},
});
References
(6) How was your day? Constructing with docker-compose.yml